OpenSWATH¶
Introduction¶
OpenSWATH [3] allows the analysis of LC-MS/MS DIA (data independent acquisition) data using the approach described by Gillet et al. [4]. The DIA approach described there uses 32 cycles to iterate through precursor ion windows from 400-426 Da to 1175-1201 Da and at each step acquires a complete, multiplexed fragment ion spectrum of all precursors present in that window. After 32 fragmentations (or 3.2 seconds), the cycle is restarted and the first window (400-426 Da) is fragmented again, thus delivering complete “snapshots” of all fragments of a specific window every 3.2 seconds. The analysis approach described by Gillet et al. extracts ion traces of specific fragment ions from all MS2 spectra that have the same precursor isolation window, thus generating data that is very similar to SRM traces.
Installation of OpenSWATH¶
OpenSWATH has been fully integrated since OpenMS 1.10 [2], [1], [5], [6], [7].
Installation of mProphet¶
mProphet[8] is available as standalone script in
mProphet will be used in this tutorial.
Generating the Assay Library¶
Generating TraML from transition lists¶
OpenSWATH requires an assay library to be supplied in the TraML format[9]. To enable manual editing of transition lists, the TOPP tool TargetedFileConverter is available, which uses tab separated files as input. Example datasets are provided in .tsv.
The header of the transition list contains the following variables (with example values in brackets):
Required Columns:
PrecursorMz
The mass-to-charge (m/z) of the precursor ion. (924.539)
ProductMz
The mass-to-charge (m/z) of the product or fragment ion. (728.99)
LibraryIntensity
The relative intensity of the transition. (0.74)
NormalizedRetentionTime
The normalized retention time (or iRT)[10] of the peptide. (26.5)
Targeted Proteomics Columns
ProteinId
A unique identifier for the protein. (AQUA4SWATH_HMLangeA)
PeptideSequence
The unmodified peptide sequence. (ADSTGTLVITDPTR)
ModifiedPeptideSequence
The peptide sequence with UniMod modifications. (ADSTGTLVITDPTR(UniMod:267))
PrecursorCharge
The precursor ion charge. (2)
ProductCharge
The product ion charge. (2)
Grouping Columns:
TransitionGroupId
A unique identifier for the transition group. (AQUA4SWATH_HMLangeA_ADSTGTLVITDPTR(UniMod:267)/2)
TransitionId
A unique identifier for the transition. (AQUA4SWATH_HMLangeA_ADSTGTLVITDPTR(UniMod:267)/2_y8)
Decoy
A binary value whether the transition is target or decoy. (target: 0, decoy: 1)
PeptideGroupLabel
Which label group the peptide belongs to.
DetectingTransition
Use transition for peak group detection. (1)
IdentifyingTransition
Use transition for peptidoform inference using IPF. (0)
QuantifyingTransition
Use transition to quantify peak group. (1)
For further instructions about generic transition list and assay library generation please see the following link. To convert transitions lists to TraML, use the TargetedFileConverter: Please use the absolute path to your OpenMS installation.
Linux or Mac
On the Terminal:
TargetedFileConverter -in OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary_woDecoy.tsv -out OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary_woDecoy.TraML
Windows
On the TOPP command:
TargetedFileConverter.exe -in OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary_woDecoy.tsv -out OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary_woDecoy.TraML
Appending decoys to a TraML file¶
In addition to the target assays, OpenSWATH requires decoy assays in the library which are later used for classification and error rate estimation. For the decoy generation it is crucial that the decoys represent the targets in a realistic but unnatural manner without interfering with the targets. The methods for decoy generation implemented in OpenSWATH include ’shuffle’, ’pseudo-reverse’, ’reverse’ and ’shift’. To append decoys to a TraML, the TOPP tool OpenSwathDecoyGenerator can be used: Please use the absolute path to your OpenMS installation.
Linux or Mac
On the Terminal:
OpenSwathDecoyGenerator -in OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary_woDecoy.TraML -out OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary.TraML -method shuffle -switchKR false
Windows
On the TOPP command:
OpenSwathDecoyGenerator.exe -in OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary_woDecoy.TraML -out OpenSWATH_SGS_AssayLibrary.TraML -method shuffle -switchKR false
OpenSWATH KNIME¶
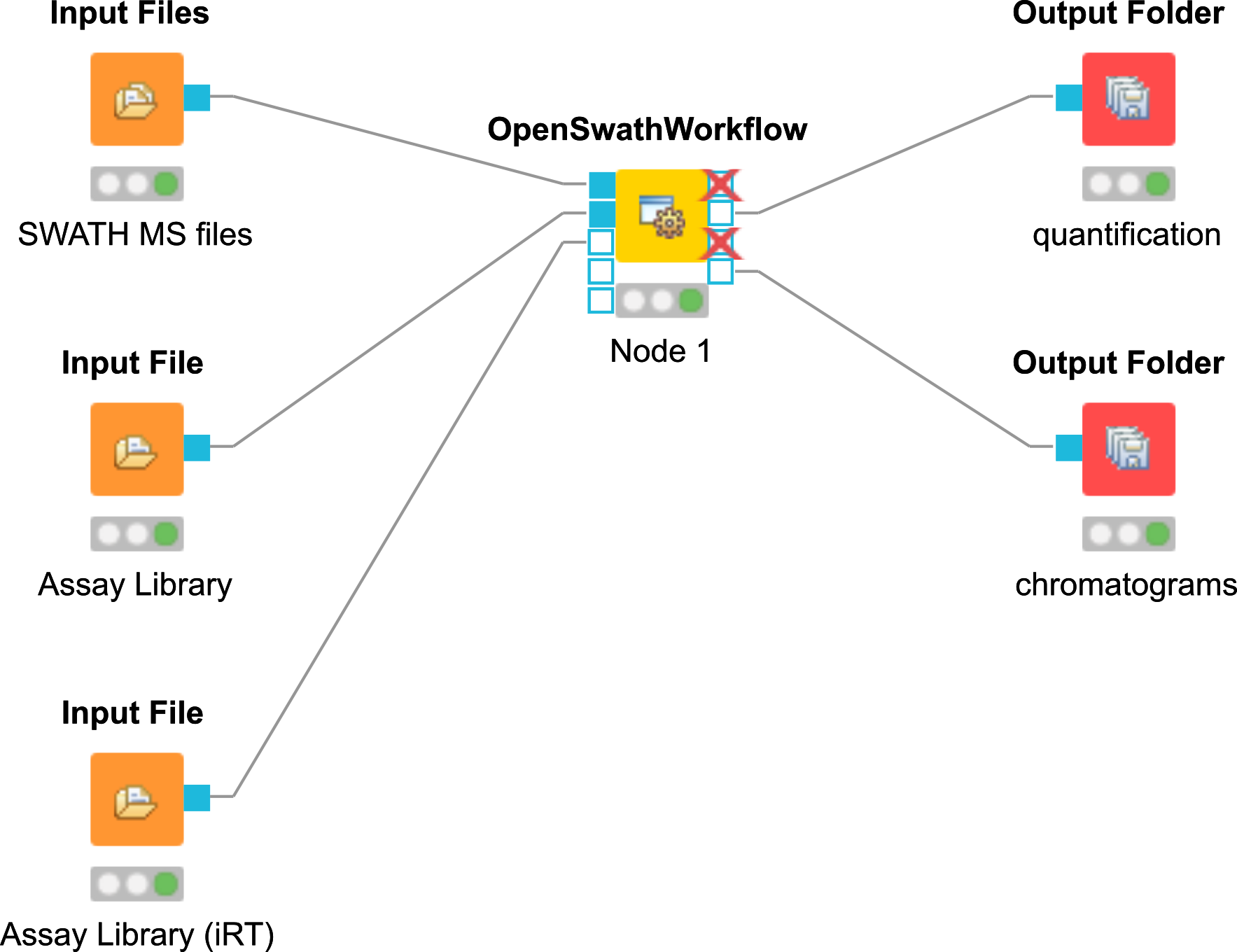
An example KNIME workflow for OpenSWATH is supplied in Workflows (Fig. 44). The example dataset can be used for this workflow (filenames in brackets):
Open
Workflows▸OpenSWATH.knwf in KNIME: File > Import KNIME Workflow…Select the normalized retention time (iRT) assay library in TraML format by double-clicking on node
File Importer> iRT Assay Library. (ExampleData▸OpenSWATH▸assay▸OpenSWATHiRTAssayLibrary.TraML ).Select the SWATH MS data in mzML format as input by double-clicking on node Input File > SWATH-MS files. (
ExampleData▸OpenSWATH▸data▸splitnapedroL120420x010SW-*.nf.pp.mzML ).Select the target peptide assay library in TraML format as input by double-clicking on node
Input Files> Assay Library. (ExampleData▸OpenSWATH▸assay▸OpenSWATHSGSAssayLibrary.TraML ).Set the output destination by double-clicking on node
Output File.Run the workflow.
The resulting output can be found at your selected path, which will be used as input for mProphet. Execute the script on the Terminal (Linux or Mac) or cmd.exe (Windows) in
R --slave --args bin_dir=../../../External_Tools/mProphet/ mquest=OpenSWATH_quant.tsv workflow=LABEL_FREE num_xval=5 run_log=FALSE write_classifier=1 write_all_pg=1 < ../../../External_Tools/mProphet/mProphet.R
or for Windows:
"C:\Program Files\R\R-3.5.1\bin\x86\R.exe" --slave --args bin_dir=../../../External_Tools/mProphet/ mquest=OpenSWATH_quant.tsv workflow=LABEL_FREE num_xval=5 run_log=FALSE write_classifier=1 write_all_pg=1 < ../../../External_Tools/mProphet/mProphet.R
The main output will be called:
Please note that due to the semi-supervised machine learning approach of mProphet the results differ slightly when mProphet is executed several times.
|
|---|
Figure 44: OpenSWATH KNIME Workflow. |
Additionally, the chromatogram output (.mzML) can be visualized for inspection with TOPPView. For additional instructions on how to use pyProphet instead of mProphet please have a look at the PyProphet Legacy Workflow. If you want to use the SQLite-based workflow in your lab in the future, please have a look here. The SQLite-based workflow will not be part of the tutorial.
From the example dataset to real-life applications¶
The sample dataset used in this tutorial is part of the larger SWATH MS Gold Standard (SGS) dataset which is described in the publication of Roest et al.[3]. It contains one of 90 SWATH-MS runs with significant data reduction (peak picking of the raw, profile data) to make file transfer and working with it easier. Usually SWATH-MS datasets are huge with several gigabyte per run. Especially when complex samples in combination with large assay libraries are analyzed, the TOPP tool based workflow requires a lot of computational resources. Additional information and instruction can be found at the following link.