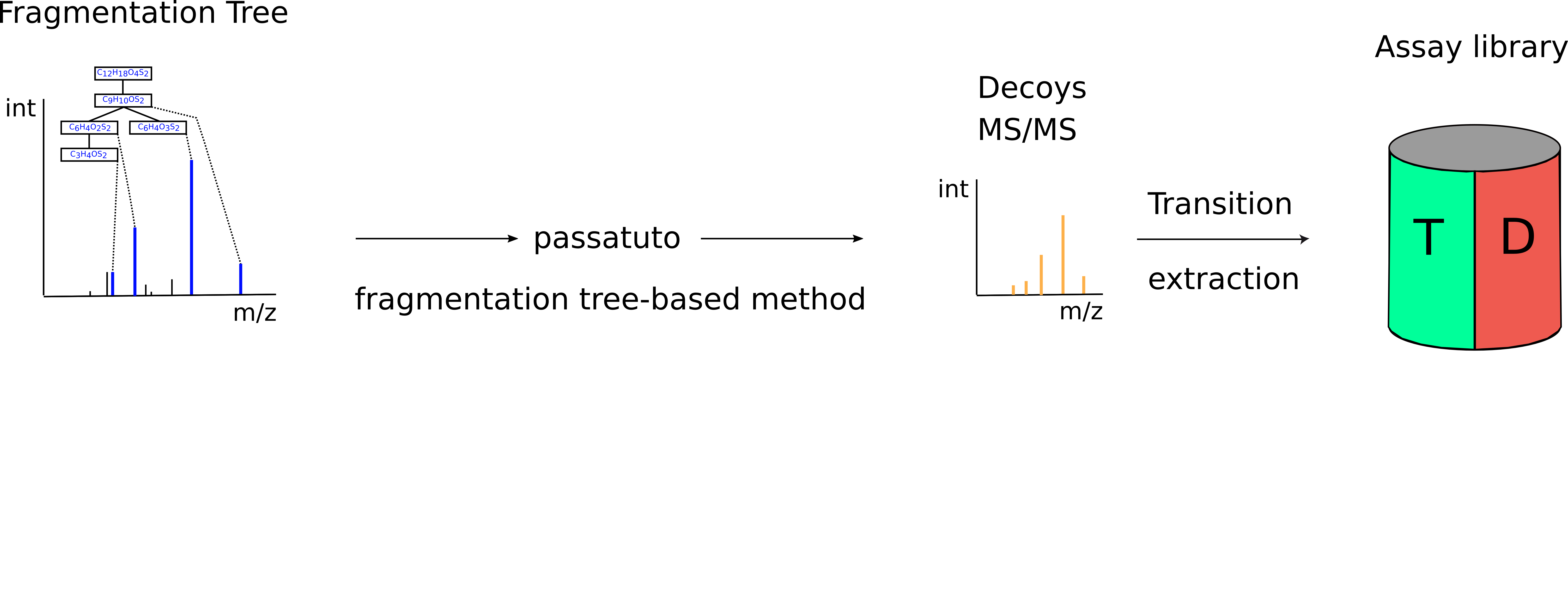OpenSWATH for Metabolomics¶
Introduction¶
We would like to present an automated DIA/SWATH analysis workflow for metabolomics, which takes advantage of experiment specific target-decoy assay library generation. This allows for targeted extraction, scoring and statistical validation of metabolomics DIA data[1], [2].
Workflow¶
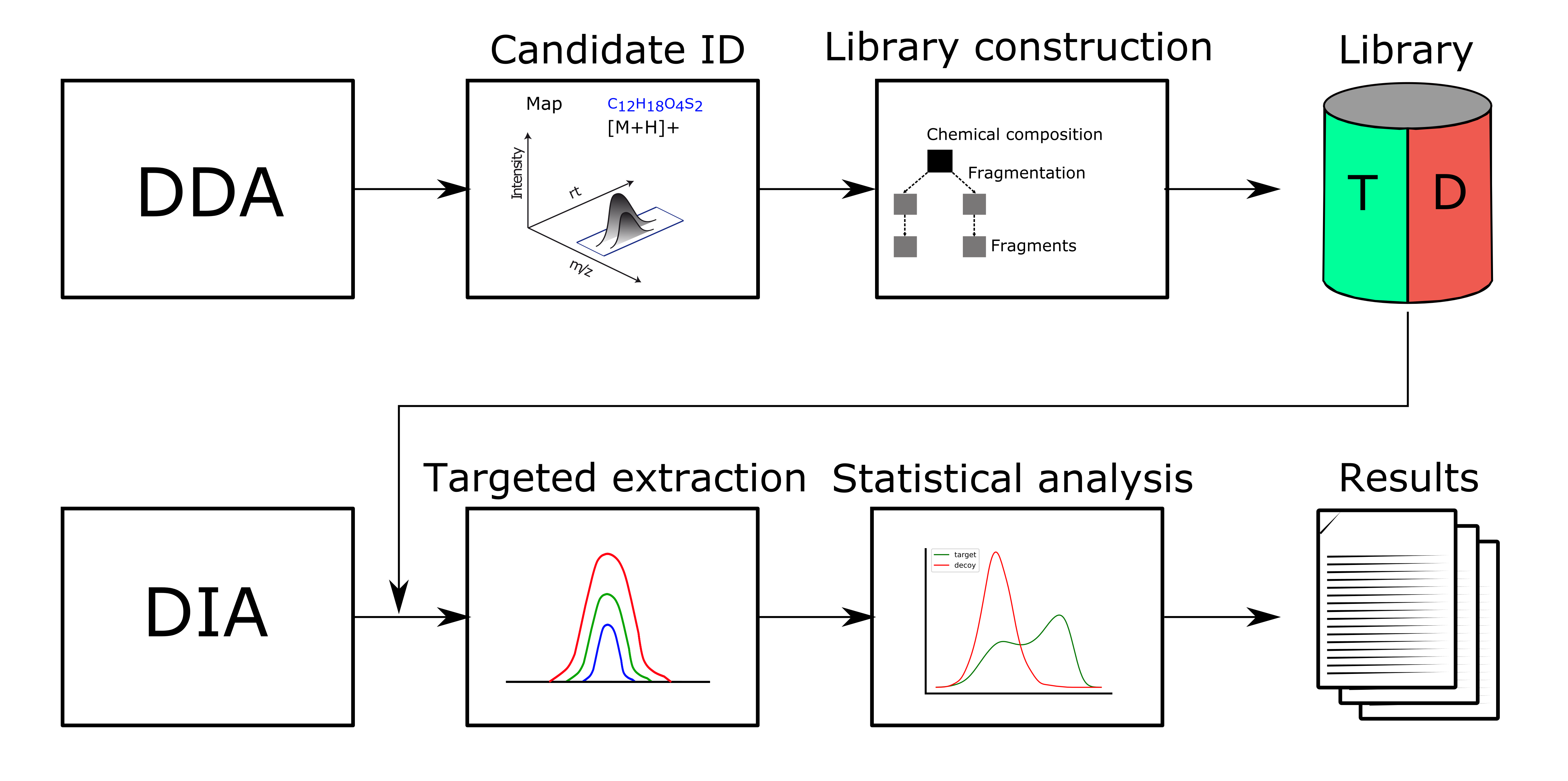
The workflow follows multiple steps (see Fig. 45).
|
|---|
Figure 45: DIAMetAlyzer - pipeline for assay library generation and targeted analysis with statistical validation. DDA data is used for candidate identification containing feature detection, adduct grouping and accurate mass search. Library construction uses fragment annotation via compositional fragmentation trees and decoy generation using a fragmentation tree re-rooting method to create a target-decoy assay library. This library is used in a second step to analyse metabolomics DIA data performing targeted extraction, scoring and statistical validation (FDR estimation). |
|
|---|
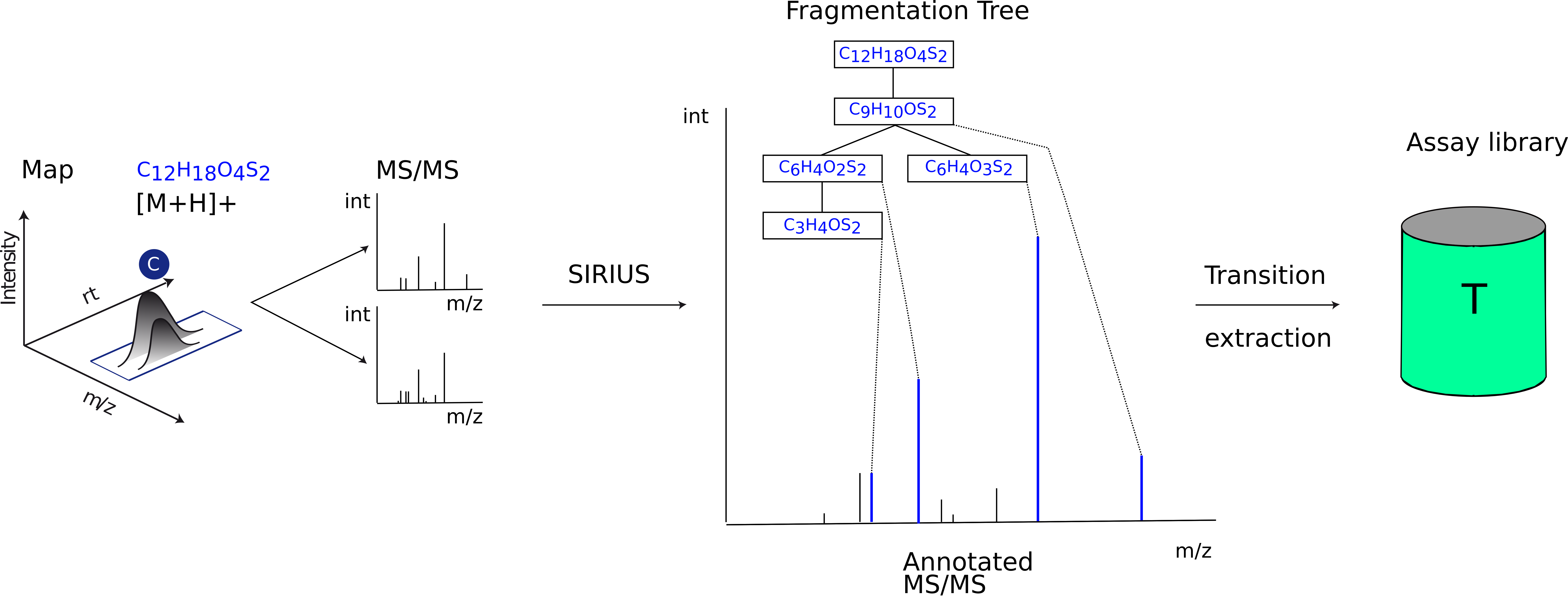
Figure 46: Assay library generation. The results of the compound identification (feature, molecular formula, adduct), with the corresponding fragment spectra for the feature, are used to perform fragment annotation via SIRIUS, using the compositional fragmentation trees. Then, the n highest intensity transitions are extracted and stored in the assay library. |
|
|---|
Figure 47: Decoy generation. The compositional fragmentations trees from the step above are used to run the fragmentation tree re-rooting method from Passatutto, generating a compound specific decoy MS2 spectrum. Here, the n highest intensity decoy transitions are extracted and stored in the target-decoy assay library. |
Candidate identification Feature detection, adduct grouping and accurate mass search are applied on DDA data.
Library construction The knowledge determined from the DDA data, about compound identification, its potential adduct and the corresponding fragment spectra are used to perform fragment annotation via compositional fragmentation trees sugin SIRIUS 4[3]. Afterwards transitions, which are the reference of a precursor to its fragment ions are stored in a so-called assay library (Fig. 46). Assay libraries usually contain additional metadata (i.e. retention time, peak intensities). FDR estimation is based on the target-decoy approach[4]. For the generation of the MS2 decoys, the fragmentation tree-based rerooting method by Passatutto ensure the consistency of decoy spectra (Fig.47)[5]. The target-decoy assay library is then used to analyse the SWATH data.
Targeted extraction Chromatogram extraction and peak-group scoring. This step is performed using an algorithm based on OpenSWATH[1] for metabolomics data.
Statistical validation FDR estimation uses the PyProphet algorithm[2]. To prevent overfitting we chose the simpler linear model (LDA) for target-decoy discrimination in PyProphet, using MS1 and MS2 scoring with low correlated scores.
Prerequisites¶
Apart from the usual KNIME nodes, the workflow uses python scripting nodes. One basic requirement for the installation of python packages, in particular pyOpenMS, is a package manager for python. Using conda as an environment manger allows to specify a specific environment in the KNIME settings (File>Preferences>KNIME>Python).
Windows¶
We suggest do use a virtual environment for the Python 3 installation on windows. Here you can install miniconda and follow the further instructions.
Create new
condapython environment.conda create -n py39 python=3.9
Activate
py39environment.conda activate py39
Install pip (see above).
On the command line:
python -m pip install -U pip python -m pip install -U numpy python -m pip install -U pandas python -m pip install -U pyprophet python -m pip install -U pyopenms
macOS¶
We suggest do use a virtual environment for the Python 3 installation on Mac. Here you can install miniconda and follow the further instructions.
Create new
condapython environment.conda create -n py39 python=3.9
Activate py39 environment.
conda activate py39
On the Terminal:
python -m pip install -U pip python -m pip install -U numpy python -m pip install -U pandas python -m pip install -U pyprophet python -m pip install -U pyopenms
Linux¶
Use your package manager apt-get or yum, where possible.
Install Pytohn 3.9 (Debian: python-dev, RedHat: python-devel)
Install NumPy (Debian/RedHat: python-numpy).
Install setuptools (Debian/RedHat: python-setuptools).
On the Terminal:
python -m pip install -U pip python -m pip install -U numpy python -m pip install -U pandas python -m pip install -U pyprophet python -m pip install -U pyopenms
Benchmark data¶
For the assay library construction pesticide mixes (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) were measured individually in solvent (DDA). Benchmark DIA samples were prepared by spiking different commercially available pesticide mixes into human plasma metabolite extracts in a 1:4 dilution series, which covers 5 orders of magnitude.
The example data can be found here.
Example workflow¶
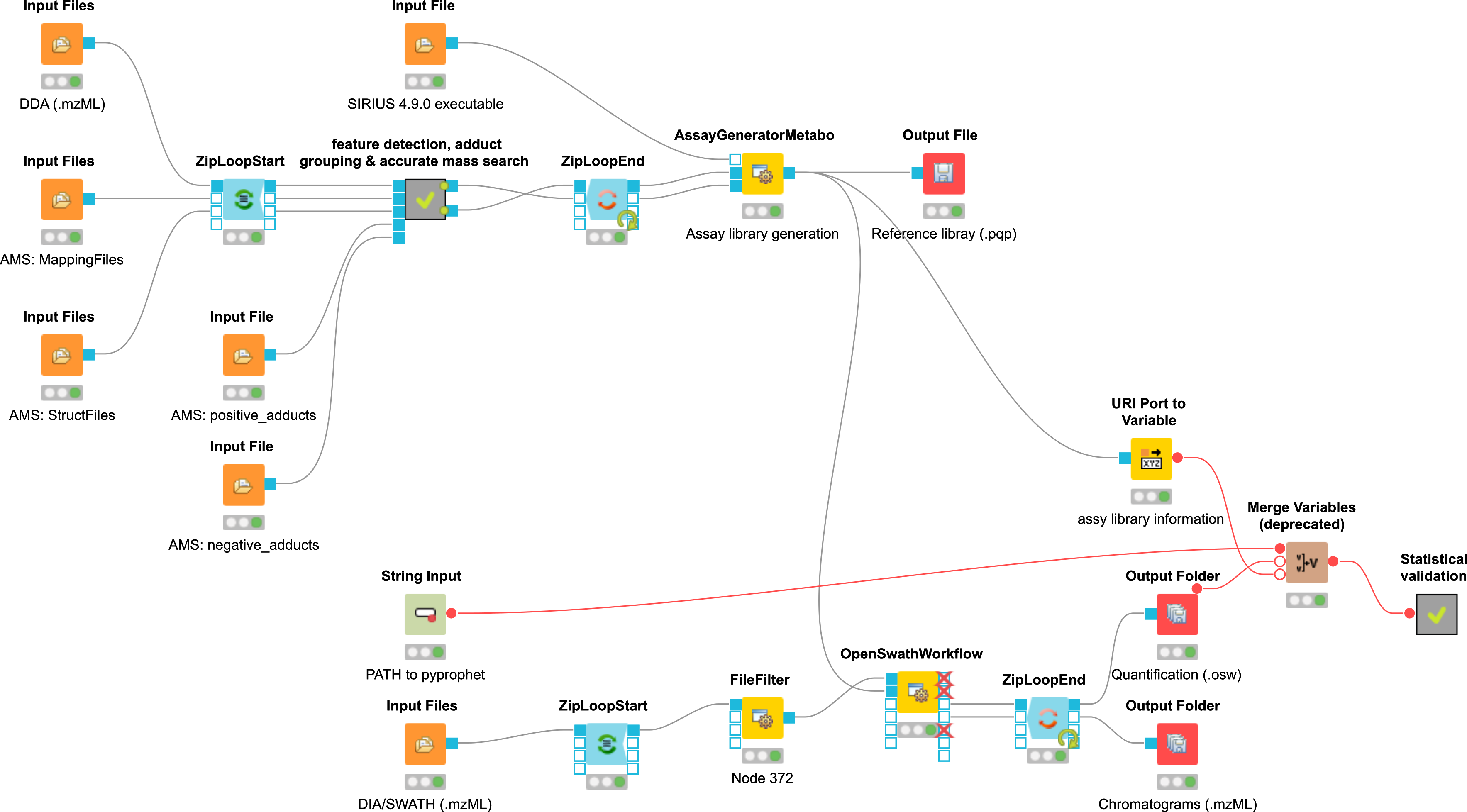
Example workflow for the usage of the DIAMetAlyzer Pipeline in KNIME (see Fig. 48). Inputs are the SWATH-MS data in profile mode (.mzML), a path for saving the new target-decoy assay library, the SIRIUS 4.9.0 executable, the DDA data (.mzML), custom libraries and adducts for AccurateMassSearch, the min/max fragment mass-to-charge to be able to restrict the mass of the transitions and the path to the PyProphet executable. The DDA is used for feature detection, adduct grouping, accurate mass search and forwarded to the AssayGeneratorMetabo. Here, feature mapping is performed to collect MS2 spectra that belong to a feature. All information collected before (feautre, adduct, putative identification, MS2 spectra) are then internally forwarded to SIRIUS. SIRIUS is used for fragment annotation and decoy generation based on the fragmentation tree re-rooting approach. This information is then used to filter spectra/decoys based on their explained intensity (min. 85%). Afterwards internal feature linking is performed which is most important for untargeted experiments using a lot of DDA data to construct the library. The constructed target-decoy assay library is processed with the SWATH-MS data in OpenSWATH. The results are used by PyProphet for scoring and output a list of metabolites with their respective q-value and quantitative information.
|
|---|
Figure 48: Example workflow for the usage of the DIAMetAlyzer Pipeline in KNIME. |
Run the workflow¶
These steps need to be followed to run the workflow successfully:
Add DDA Input Files (.mzML).
Specify SIRIUS 4.9.0 executable.
Specify library files (mapping, struct) for AccurateMassSearch.
Add positive/negative adducts lists for AccurateMassSearch.
Supply an output path for the SIRIUS workspace in the AssayGeneratorMetabo.
Specify additional paths and variables, such as an output path for the target-decoy assay library and a path to the pyprophet installation as well as decoy fragment mz filter (min/max).
Input DIA/SWATH files (.mzML).
Specify output path in the output folders.
You can now run the workflow.
Important parameters¶
Please have a look at the most important parameters, which should be tweaked to fit your data. In general, OpenMS has a lot of room for parameter optimization to best fit your chromatography and instrumental settings.
FeatureFinderMetabo¶
parameter |
explanation |
|---|---|
noise_threshold_int |
Intensity threshold below which peaks are regarded as noise. |
chrom_fwhm |
Expected chromatographic peak width (in seconds). |
mass_error_ppm |
Allowed mass deviation (in ppm). |
MetaboliteAdductDecharger¶
parameter |
explanation |
|---|---|
mass_max_diff |
Maximum allowed mass tolerance per feature… |
potential_adducts |
Adducts used to explain mass differences - These should fit to the adduct list specified for AccurateMassSearch. |
AccurateMassSearch¶
parameter |
explanation |
|---|---|
mass_error_value |
Tolerance allowed for accurate mass search. |
ionization_mode |
Positive or negative ionization mode. |
AssayGeneratorMetabo¶
parameter |
explanation |
|---|---|
min_transitions |
Minimal number of transitions (3). |
max_transitions |
Maximal number of transitions (3). |
min_fragment_mz |
Minimal m/z of a fragment ion choosen as a transition |
max_fragment_mz |
Maximal m/z of a fragment ion choosen as a transition |
transitions_threshold |
Further transitions need at least x% of the maximum intensity. |
fragment_annotation_score_threshold |
Filters annotations based on the explained intensity of the peaks in a spectrum (0.8). |
SIRIUS (internal): |
|
out_workspace_directory |
Output directory for SIRIUS workspace (Fragmentation Trees). |
filter_by_num_masstraces |
Features have to have at least x MassTraces. To use this parameter feature_only is neccessary. |
precursor_mass_tolerance |
Tolerance window for precursor selection (Feature selection in regard to the precursor). |
precursor_rt_tolerance |
Tolerance allowed for matching MS2 spectra depending on the feature size (should be around the FWHM of the chromatograms). |
profile |
Specify the used analysis profile (e.g. qtof). |
elements |
Allowed elements for assessing the putative sumformula (e.g. CHNOP[5]S[8]Cl[1]). Elements found in the isotopic pattern are added automatically, but can be specified nonetheless. |
Feature linking (internal): |
|
ambiguity_resolution mz_tolerance |
M/z tolerance for the resolution of identification ambiguity over multiple files - Feature linking m/z tolerance. |
ambiguity_resolution rt_tolerance |
RT tolerance in seconds for the resolution of identification ambiguity over multiple files - Feature linking m/z tolerance. |
total_occurrence_filter |
Filter compound based on total occurrence in analysed samples. |
In case of the total_occurrence_filter the value to chose depends on the analysis strategy used. In the instance you are using only identified compounds (use_known_unknowns= false) - it will filter based on identified features. This means that even if the feature was detected in e.g. 50% of all samples it might be only identified correctly by accurate mass search in 20% of all samples. Using a total_occurrence_filter this specific feature would still be filtered out due to less identifications.
OpenSWATH¶
parameter |
explanation |
|---|---|
rt_extraction_window |
Extract x seconds around this value. |
rt_normalization_factor |
Please use the range of your gradient e.g. 950 seconds. |
If you are analysing a lot of big DIA mzML files ≈ 3-20GB per File, it makes sense to change how OpenSWATH processes the spectra.
parameter |
explanation |
|---|---|
readOptions |
Set cacheWorkingInMemory - will cache the files to disk |
and read SWATH-by-SWATH into memory |
|
tempDirectory |
Set a directory, where cached mzMLs are stored (be |
aware that his directory can be quite huge depending on the data). |
In the workflow pyprophet is called after OpenSWATH, it merges the result files, which allows to get enough data for the model training.
pyprophet merge --template path_to_target-decoy_assay_library.pqp --out merged.osw,→ ./*.osw
Afterwards, the results are scored using the MS1 and MS2 levels and filter for metabolomics scores, which have a low correlation.
pyprophet score --in merged.osw --out scored.osw --level ms1ms2 --ss_main_score,→ ”var_isotope_correlation_score” --ss_score_filter metabolomics
Export the non filtered results:
pyprophet export-compound --in scored.osw --out scored + ”_pyprophet_nofilter_ms1ms2.tsv” --max_rs_peakgroup_qvalue 1000.0
Please see the workflow for actual parameter values used for the benchmarking dataset.
The workflow can be used without any identification (remove AccurateMassSearch). Here, all features (known_unknowns) are processed. The assay library is constructed based on the chemical composition elucidated via the fragment annotation (SIRIUS 4). It is also possible to use identified and in addition unknown (non-identified) features, by using AccurateMassSearch in combination with the use_known_unknowns in the AssayGeneratorMetabo.